Gardner's Theory
of Multiple Intelligences
By Kendra Cherry
When you hear the word intelligence, the concept of IQ testing may immediately come to mind. Intelligence is often defined as our intellectual potential; something we are born with, something that can be measured, and a capacity that is difficult to change. In recent years, however, other views of intelligence have emerged. One such conception is the theory of multiple intelligences proposed by Harvard psychologist Howard Gardner.
Theory of Multiple Intelligences
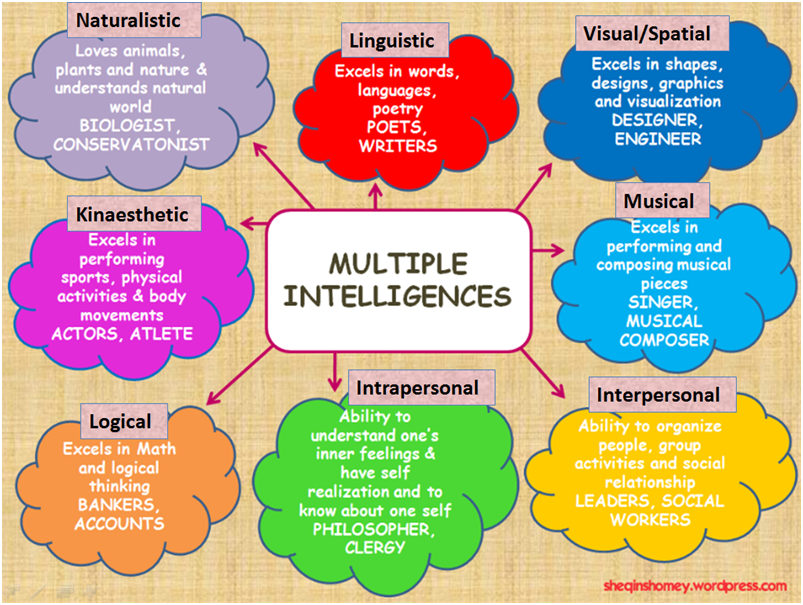
This theory suggests that traditional psychometric views of intelligence are too limited. Gardner first outlined his theory in his 1983 book "Frames of Mind: The Theory of Multiple Intelligences," where he suggested that all people have different kinds of "intelligences." Gardner proposed that there are eight intelligences, and has suggested the possible addition of a ninth known as "existentialist intelligence."
In order to capture the full range of abilities and talents that people possess, Gardner theorizes that people do not have just an intellectual capacity, but have many kinds of intelligence, including musical, interpersonal, spatial-visual, and linguistic intelligences.
While a person might be particularly strong in a specific area, such as musical intelligence, he or she most likely possesses a range of abilities. For example, an individual might be strong in verbal, musical, and naturalistic intelligence.
Criticism
Gardner’s theory has come under criticism from both psychologists and educators. These critics argue that Gardner’s definition of intelligence is too broad and that his eight different "intelligences" simply represent talents, personality traits, and abilities. Gardner’s theory also suffers from a lack of supporting empirical research.
Despite this, the theory of multiple intelligences enjoys considerable popularity with educators. Many teachers utilize multiple intelligences in their teaching philosophies and work to integrate Gardner’s theory into the classroom.
Learning more about the multiple intelligences can help you better understand your own strengths. Continue reading to learn more about the major characteristics of each type of intelligence, and if you still aren't sure which type describes you best, this quiz can help you figure it out.
1
Visual-Spatial Intelligence
Strengths: Visual and spatial judgment
People who are strong in visual-spatial intelligence are good at visualizing things. These individuals are often good with directions as well as maps, charts, videos, and pictures.
Characteristics
Characteristics of visual-spatial intelligence include:
- Enjoys reading and writing
- Good at putting puzzles together
- Good at interpreting pictures, graphs, and charts
- Enjoys drawing, painting, and the visual arts
- Recognizes patterns easily
Potential Career Choices
If you're strong in visual-spatial intelligence, good career choices for you are:
- Architect
- Artist
- Engineer
2
Linguistic-Verbal Intelligence
Strengths: Words, language, and writing
People who are strong in linguistic-verbal intelligence are able to use words well, both when writing and speaking. These individuals are typically very good at writing stories, memorizing information, and reading.
Characteristics
Characteristics of linguistic-verbal intelligence include:
- Good at remembering written and spoken information
- Enjoys reading and writing
- Good at debating or giving persuasive speeches
- Able to explain things well
- Often uses humor when telling stories
Potential Career Choices
If you're strong in linguistic-verbal intelligence, good career choices for you are:
- Writer/journalist
- Lawyer
- Teacher
3
Logical-Mathematical Intelligence
Strengths: Analyzing problems and mathematical operations
People who are strong in logical-mathematical intelligence are good at reasoning, recognizing patterns, and logically analyzing problems. These individuals tend to think conceptually about numbers, relationships, and patterns.
Characteristics
Characteristics of logical-mathematical intelligence include:
- Excellent problem-solving skills
- Enjoys thinking about abstract ideas
- Likes conducting scientific experiments
- Good at solving complex computations
Potential Career Choices
If you're strong in logical-mathematical intelligence, good career choices for you are:
- Scientist
- Mathematician
- Computer programmer
- Engineer
- Accountant
4
Bodily-Kinesthetic Intelligence
Strengths: Physical movement, motor control
Those who have high bodily-kinesthetic intelligence are said to be good at body movement, performing actions, and physical control. People who are strong in this area tend to have excellent hand-eye coordination and dexterity.
Characteristics
Characteristics of bodily-kinesthetic intelligence include:
- Good at dancing and sports
- Enjoys creating things with his or her hands
- Excellent physical coordination
- Tends to remember by doing, rather than hearing or seeing
Potential Career Choices
If you're strong in bodily-kinesthetic intelligence, good career choices for you are:
- Dancer
- Builder
- Sculptor
- Actor
5
Musical Intelligence
Strengths: Rhythm and music
People who have strong musical intelligence are good at thinking in patterns, rhythms, and sounds. They have a strong appreciation for music and are often good at musical composition and performance.
Characteristics
Characteristics of musical intelligence include:
- Enjoys singing and playing musical instruments
- Recognizes musical patterns and tones easily
- Good at remembering songs and melodies
- Rich understanding of musical structure, rhythm, and notes
Potential Career Choices
If you're strong in musical intelligence, good career choices for you are:
- Musician
- Composer
- Singer
- Music teacher
- Conductor
6
Interpersonal Intelligence
Strengths: Understanding and relating to other people
Those who have strong interpersonal intelligence are good at understanding and interacting with other people. These individuals are skilled at assessing the emotions, motivations, desires, and intentions of those around them.
Characteristics
Characteristics of interpersonal intelligence include:
- Good at communicating verbally
- Skilled at nonverbal communication
- Sees situations from different perspectives
- Creates positive relationships with others
- Good at resolving conflict in groups
Potential Career Choices
If you're strong in interpersonal intelligence, good career choices for you are:
- Psychologist
- Philosopher
- Counselor
- Salesperson
- Politician
7
Intrapersonal Intelligence
Strengths: Introspection and self-reflection
Individuals who are strong in intrapersonal intelligence are good at being aware of their own emotional states, feelings, and motivations. They tend to enjoy self-reflection and analysis, including daydreaming, exploring relationships with others, and assessing their personal strengths.
Characteristics
Characteristics of intrapersonal intelligence include:
- Good at analyzing his or her strengths and weaknesses
- Enjoys analyzing theories and ideas
- Excellent self-awareness
- Clearly understands the basis for his or her own motivations and feelings
Potential Career Choices
If you're strong in intrapersonal intelligence, good career choices for you are:
- Philosopher
- Writer
- Theorist
- Scientist
8
Naturalistic Intelligence
Strengths: Finding patterns and relationships to nature
Naturalistic is the most recent addition to Gardner’s theory and has been met with more resistance than his original seven intelligences. According to Gardner, individuals who are high in this type of intelligence are more in tune with nature and are often interested in nurturing, exploring the environment, and learning about other species. These individuals are said to be highly aware of even subtle changes to their environments.
Characteristics
Characteristics of naturalistic intelligence include:
- Interested in subjects such as botany, biology, and zoology
- Good at categorizing and cataloging information easily
- May enjoy camping, gardening, hiking, and exploring the outdoors
- Doesn’t enjoy learning unfamiliar topics that have no connection to nature
Potential Career Choices
If you're strong in naturalistic intelligence, good career choices for you are:
- Biologist
- Conservationist
- Gardener
- Farmer
Proprioceptiveby Middletown Centre for Autism
Sensory IntegrationBy Cindy Hatch-Rasmussen, M.A., OTR/L
Learning Disabilities and Disordersby Authors: Gina Kemp, M.A., Melinda Smith, M.A., and Jeanne Segal, Ph.D. Last updated: March 2018.
ADHD in Childrenby Authors: Melinda Smith, M.A., Lawrence Robinson, and Jeanne Segal, Ph.D. Last updated: March 2018.
Does My Child Have Autism?By Authors: Melinda Smith, M.A., Jeanne Segal, Ph.D., and Ted Hutman, Ph.D. Last updated: March 2018.
Autism Behavior Problems What's Triggering Your Child's Outbursts?Adapted with permission from The Autism Revolution by Martha Herbert, M.D., Ph.D., with Karen Weintraub.
Executive Function Disorder, Explained!by Larry Silver, M.D.
- Gardner H. Intelligence Reframed: Multiple Intelligences for the 21st Century. New York: Basic Books; 1999.
- Gardner H. A Multiplicity of Intelligences. Published 2004.
- Gardner H. Frames of Mind: The Theory of Multiple Intelligences. New York: Basic Books; 1983.
- Gardner H. On the Three Faces of Intelligence. Daedalus.Winter 2002;131(1):139-142.
-
Brain Development and Executive Functioningby Katie Knapp, MSc, J. Bruce Morton, PhD Western University, Canada
Why Kids With Executive Functioning Issues Have Trouble With PlanningBy Kate Kelly
Brain Development and Executive Functioningby Katie Knapp, MSc, J. Bruce Morton, PhD Western University, Canada
Why Kids With Executive Functioning Issues Have Trouble With PlanningBy Kate Kelly
Executive Functioning – Where is it Controlled and How Does it Develop?/ emediation Techniques for Deficits and Dysfunction By : Angie McCalla , MS, CCC-SLP, CBIS
